Boolean operators can help students, faculty, and other people conduct research with a bit more ease. Using Boolean operators coupled with using synonyms for your search terms can reduce stress and ensure that you are getting the maximum benefit from your research time.
AND
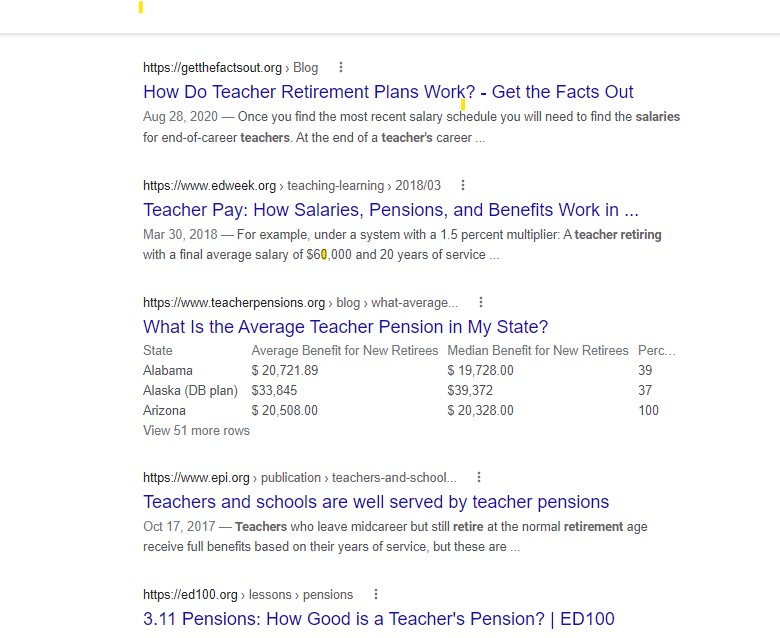
AND is one of the most common Boolean operators. Using AND can narrow a search by combining terms. For example, combining terms such as those below will result in search documents and other resources with all of the terms in the returned search items.
teacher AND pay AND retirement

OR
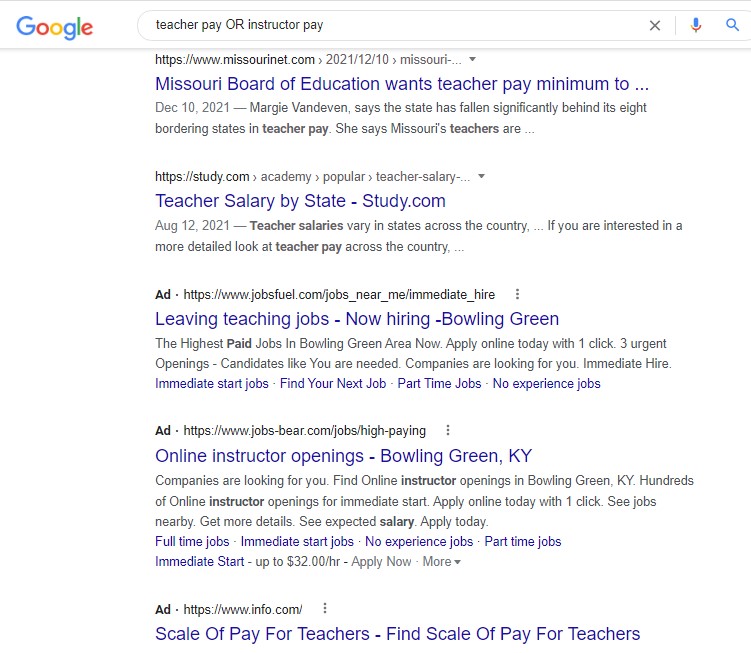
OR is a Boolean operator that broadens a search. It can be used with synonyms or with unrelated terms. For example, if the search is as shown below, the search engine will find results about teacher OR instructor pay. Simple and effective.
teacher pay OR instructor pay
Truncation
Truncation is a research technique that typically uses an asterisk. The asterisk is added to a word to search for other words that are similar but have different endings. This works especially for most databases. Please note that some databases use different symbols, so contact the library when in doubt. Most college libraries can tell you what symbol is used.
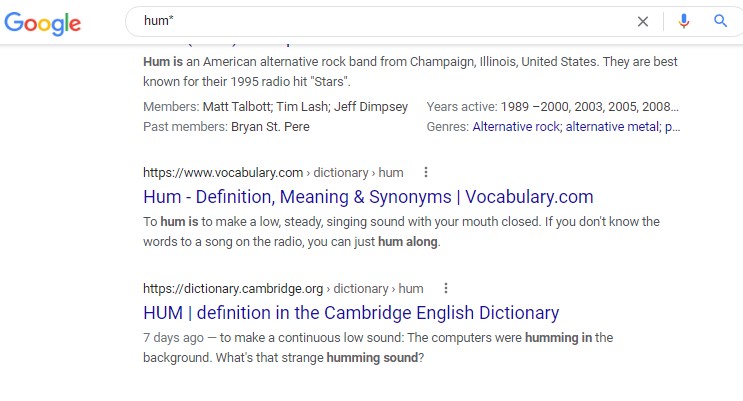
An example of using the asterisk for research is: hum* “Hum with an asterisk will tell the search engine to search for words that have “hum” in them. This my or my not work for search engines. For example, consider the search below.
Wildcard
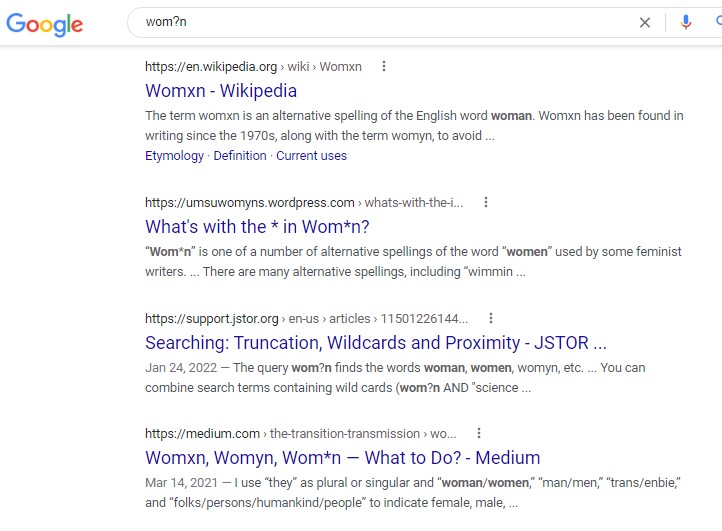
A wildcard is used to replace a letter in most database and search engine searches. Most of the time, the ? symbol can be used to replace a letter in a word to yield a wider range of words by replacing the ? with different letters in the search results. Note that # may also be used. Consider the following:
NOT
Left for last, NOT is not always the best Boolean phrase to use to do searches. While NOT doesn’t work as well with search engines, it works with most database searches. The Google search engine typically doesn’t recognize the NOT function. For example, putting in the following yields an entire list of results about Corvettes.
Cars NOT Corvettes
Because Google searches yield information about Corvettes, the screenshot was not included. In most databases using the phrase above will result in results about cars. It will exclude Corvettes.
Conclusion
Research can be a fairly lengthy process, so using simple techniques is important to reduce stress and gain helpful results. Note that using Boolean phrases can only help when a researcher uses good keywords. So, make sure you use good keywords in your searches for best results.
